Postgraduate Degree in Fetal Cardiology

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
- PRESENTATION
- OBJECTIVES
- INFORMATION OF INTEREST
- TEACHING STRUCTURE
2. ACADEMIC PROGRAM
MODULE 1: FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
MODULE 2: SEPTAL DEFECTS
MODULE 3: LEFT CHD
MODULE 4: RIGHT CHD
MODULE 5: CONOTRUNCAL ANOMALIES
MODULE 6: COMPLEX CHD-OTHER CARDIAC ANOMALIES
MODULE 7: VASCULAR / VENOUS SYSTEM ANOMALIES
MODULE 8: FETAL ARRHYTHMIAS AND FETAL CARDIAC THERAPY
MODULE 9: FETAL HEART ADAPTATION TO EXTRA-CARDIAC CONDITIONS / NOVEL TECHNOLOGIES
MODULE 10: RESEARCH PROJECT
3. COMPLEMENTARY TOOLS
MASTERCLASSES
RESOLUTION OF CLINICAL CASES
FORUM
RULES FOR THE USE OF THE FORUM
4. PRACTICE AT HOME
IMAGE LIST AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA
5. FACE TO FACE PERIOD
6. RESEARCH PROJECT (MODULE 10)
7. EVALUATION CRITERIA
*******************************************************
1-GENERAL INFORMATION
PRESENTATION
The aim of this program is to improve your skills and achieve excellence in the fetal diagnosis and management of congenital heart defects (CHD) as well as in the morphological and functional evaluation of the fetal heart in different clinical conditions.
A comprehensive approach from pathophysiology to detailed imaging, the acquisition of knowledge is achieved through intensive exposure to a large number of clinical cases representing all possible conditions and situations found in a fetal cardiology unit.
With a better clinical decision-making, masterclasses and a face-to-face period in clinic are designed to complement the specific skills in the performance of high-quality echocardiography and the evaluation of prognosis, with skills in multidisciplinary management and parental counseling. The online practical part aims to complement the theoretical training and submitting certain images in order to validate the new competencies. Therefore, the interactive program provides an opportunities to take part in open discussions via a forum, sharing your own cases with experts.
Two onsite weeks at the clínic will enable close interactions with the experts , workshops on new technologies and practical training.
Target audience
Fetal cardiology training for fetal medicine specialists and ultrasound professionals with experience in fetal echocardiography who want to improve their understanding and clinical skills on fetal cardiology
OBJECTIVES
Academic goal
- To enable participants to perform expert diagnosis and counseling of fetal heart anomalies by in-depth of fetal cardiac physiology
Specific objectives
- To achieve optimal acquisition of images for the evaluation of fetal cardiac morphology and it’s function
- To efficiently incorporate all related techniques, including 2D, M-mode, color and spectral Doppler, 4D-STIC, tissue Doppler, strain, and magnetic resonance to fetal echocardiographic evaluation
- To enable participants to increase the ability for diagnosis and counseling of fetal heart anomalies and fetal arrhythmias
- To enable participants to properly assess fetal cardiac function in a clinical context
- To recognize the indications, limitations, and benefits of in utero cardiac therapy in a clinical context
- To learn how the fetal heart adapts to an insult, and the consequent fetal cardiac remodeling, dysfunction and failure
- To Support the family with the emotional needs of parents facing a diagnosis of a heart anomaly
TRAINING STRUCTURE
The Postgraduate Degree in Fetal Cardiology comprises nine theoretical-practical modules including cardiac imaging, advanced knowledge on CHD and arrhythmias, and understanding on fetal cardiac function and fetal therapy.
The online modules include lectures based on clinical cases, an interactive forum and a live masterclass with experts. Each module will be complemented with the resolution of a practical clinical cases in the forum. The clinical case is based on a real case that will be discussed during the masterclass. Modules will be evaluated by an online final exam.
The practical part of the postgraduate program is designed for the students to acquire the necessary skills to perform an advanced fetal echocardiography, including a complete morphometric and functional evaluation of the fetal heart. To complete this practical part, the students will need to send more than 70 images and echocardiographic measurements from three different fetuses. These images will be evaluated and scored by the committee with a personalized feedback that will allow them to improve their skills. It will also be required to submit 5 documented cases of congenital heart defects diagnosed by the student at workplace. Also additionally, at the time of onsite training, the students will have the opportunity to participate in hands-on workshops with close supervision by the directors enabling to learn tips and tricks for an optimal acquisition.
The postgraduate training includes the completion of a research work under the supervision of a mentor.
2-ACADEMIC PROGRAM
MODULE 1: HEART EXAMINATION ONLINE CLASSES
| MODULE 2: SEPTAL DEFECTS ONLINE CLASSES
|
MODULE 3: LEFT CHD ONLINE CLASSES
| MODULE 4: RIGHT CHD ONLINE CLASSES
|
MODULE 5: CONOTRUNCAL ANOMALIES ONLINE CLASSES
| MODULE 6: OTHER CARDIAC ANOMALIES ONLINE CLASSES
|
MODULE 7: VASCULAR / VENOUS SYSTEM ANOMALIES ONLINE CLASSES
| MODULE 8: FETAL ARRHYTHMIAS AND FETAL CARDIAC THERAPY FETAL ARRHYTHMIAS ONLINE CLASSES
FETAL CARDIAC INTERVENTION ONLINE CLASSES
|
MODULE 9: FETAL HEART ADAPTATION TO EXTRA-CARDIAC CONDITIONS / NOVEL TECHNOLOGIES ONLINE CLASSES
| MODULE 10: RESEARCH PROJECT TUTORS: Cihat Sen and Ender Ödemiş |
3-COMPLEMENTARY TOOLS
MASTERCLASSES
At the end of each theoretical module, a Masterclass will be given by the coordinator of each module, with the aim of deepen the topics and the knowledge acquired from the theoretical classes. These sessions will be in streaming and the students will be able to solve their doubts with the experts online.
FORUM
An online forum is planned for each module. The forum will be supervised by the webmaster, who will ensure its correct use and functionality and it will be the tool for sharing questions and doubts regarding the studied topics and cases.
- The students to be up to date on the messages and try to answer their colleagues’ questions. There will be a teacher that will be present as moderator and may intervene if no student can help with a question.
- Before asking a question, please make sure that the topic is appropriate for that discussion forum and that the same question has not been asked before; if this happens, the repeated question will be deleted by the webmaster. Any unrelated question will be deleted to keep the forums organized
- New messages should be short, concise and self- explanatory and not any administrative or technical related questions should be asked in the forums (for example: I can’t watch the videos; I can’t download the presentations…) which will be deleted.
- Those questions that remain pending will be discussed in the following masterclass.
4-PRACTICE AT HOME
All the modules include a practical part that consists of a certain number of ultrasound images that must meet the criteria explained in the theoretical classes which has to be taken in his/her own clinical practice and submitted to the coordinator for evaluation, just after each module.
These images will be assessed and scored by the tutors, then he students will receive a evaluation feedback that will allow them to detect possible pitfalls in order to improve their skills.
These practices requires more dedication by the student to improve his/her performance in ultrasound scanning during his/her daily clinical practice.
GENERAL GUIDELINES
1. Images should be submitted from 3 different patients for every required image in each module. Images from the same patient can be used in different modules and not necessary to obtain the whole set of images of each module from the same patient. Patient names or any identity related data should not be seen on the submitted images.
2. The evaluation criteria are described in the theoretical part of the course.
3. For accreditation, at least 70% of the images must meet at least 70% of the defined criteria.
4. All the images for each module must be submitted in a single PDF document, displayed in the requested order for each module with a max. 25 MB.
5. In order to preserve the confidentiality of the patients, the submitted images must NOT show patient names or any identity related data.
IMAGE LIST AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA CARDIAC MORPHOLOGY
MODULE 1
As total: 9 images x 3 patients = 27 images
HEART
 2. Cardiac Sphericity index: It is measured in a 4-chamber view at end-diastole (value and z-score). 2. Cardiac Sphericity index: It is measured in a 4-chamber view at end-diastole (value and z-score). |
4 CHAMBER VIEW
 3. Apical view (2d): showing right/left atria and right/left ventricles at end-diastole. 3. Apical view (2d): showing right/left atria and right/left ventricles at end-diastole. |  4. Apical view (color Doppler): showing atrioventricular valvular flows at mid-diastole. 4. Apical view (color Doppler): showing atrioventricular valvular flows at mid-diastole. |
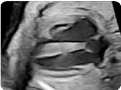 5.Transverse view (2D): showing interatrial/interventri- cular septum 5.Transverse view (2D): showing interatrial/interventri- cular septum | 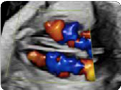 6.Transverse view (color Doppler): with adequate color scale to demonstrate the integrity of the interventri- cular septum. 6.Transverse view (color Doppler): with adequate color scale to demonstrate the integrity of the interventri- cular septum. |
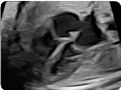 7. Basal view (2D): showing atrioventricular septum or integrity of the heart cross. 7. Basal view (2D): showing atrioventricular septum or integrity of the heart cross. | 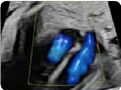 8. Basal view (color Doppler): demonstrating the absence of atrioventricular valvular insufficiency. 8. Basal view (color Doppler): demonstrating the absence of atrioventricular valvular insufficiency. |
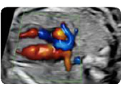 9. Pulmonary veins (color Doppler): at least two (1 left and 1 right) 9. Pulmonary veins (color Doppler): at least two (1 left and 1 right) |
MODULE 2
As total 12 images x 3 patients = 36 images
4 CHAMBER VIEW
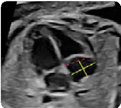 1. Atrial dimensions, atrial sphericity index (2D): maxi- mum diameters (end-systole) (value and z-score) 1. Atrial dimensions, atrial sphericity index (2D): maxi- mum diameters (end-systole) (value and z-score) | 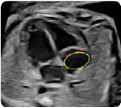 2. Atrial dimensions (2D): Area (at end-systole) (value and z-score) 2. Atrial dimensions (2D): Area (at end-systole) (value and z-score) |
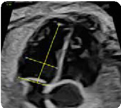 3. Ventricular dimensions, ventricular sphericity in- dex: basal, mid-transverse and longitudinal diame- ters (at end-diastole) (value and z-score) 3. Ventricular dimensions, ventricular sphericity in- dex: basal, mid-transverse and longitudinal diame- ters (at end-diastole) (value and z-score) | 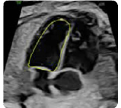 4. Ventricular dimensions: Areas (at end-diastole) (value and z-score) 4. Ventricular dimensions: Areas (at end-diastole) (value and z-score) |
LEFT VENTRICLE OUTFLOW
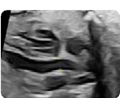 5. Left ventricle outflow tract (2d) Aortic valve: open valve (mid-systole) (value and z-score) 5. Left ventricle outflow tract (2d) Aortic valve: open valve (mid-systole) (value and z-score) | 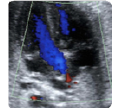 6.Left ventricle outflow tract (color Doppler): confir- ming continuity between the upper interventricular setpum and the anterior wall of the aorta. 6.Left ventricle outflow tract (color Doppler): confir- ming continuity between the upper interventricular setpum and the anterior wall of the aorta. |
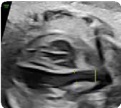 7. Ascending aorta: five-chamber view (distal portion artery) (value and z-score) 7. Ascending aorta: five-chamber view (distal portion artery) (value and z-score) |
RIGHT VENTRICLE OUTFLOW
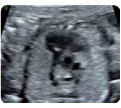 8.Right ventricle outflow tract (2D): pulmonary valve/ Open valve (mid-systole). Pulmonary valve: (value and z-score) 8.Right ventricle outflow tract (2D): pulmonary valve/ Open valve (mid-systole). Pulmonary valve: (value and z-score) | 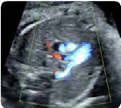 9. Right ventricle outflow tract (color Doppler): 3 ves- sel view showing a transverse section of the aorta and superior vena cava. 9. Right ventricle outflow tract (color Doppler): 3 ves- sel view showing a transverse section of the aorta and superior vena cava. |
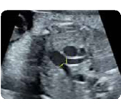 10. Pulmonary arteries (2D): at its bifurcation (value and z-score) 10. Pulmonary arteries (2D): at its bifurcation (value and z-score) | 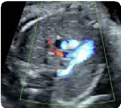 11. Pulmonary arteries (color Doppler) 11. Pulmonary arteries (color Doppler) |
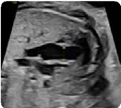 12. Pulmonary trunk: at the 3 vessel view (value and z-score) 12. Pulmonary trunk: at the 3 vessel view (value and z-score) |
MODULE 3
Total 10 images x 3 patients = 30 images3
3-VESSEL AND TRACHEA VIEW
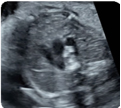 1-Apical view (2D): Ductus arteriosus (value and z-score), Aortic isthmus (value and z-score), Superior vena cava and trachea. 1-Apical view (2D): Ductus arteriosus (value and z-score), Aortic isthmus (value and z-score), Superior vena cava and trachea. | 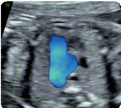 2-Apical view (color Doppler): showing anterograde and symmetrical flows. 2-Apical view (color Doppler): showing anterograde and symmetrical flows. |
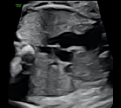 3-Transverseview(2D): Ductus arteriosus, aortic isthmus, superior vena cava and trachea 3-Transverseview(2D): Ductus arteriosus, aortic isthmus, superior vena cava and trachea | 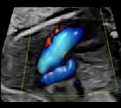 4-Transverse view (color Doppler) 4-Transverse view (color Doppler) |
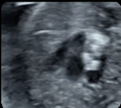 5- Basal view (2D): Ductus arteriosus, aortic Isthmus, superior vena cava and trachea. 5- Basal view (2D): Ductus arteriosus, aortic Isthmus, superior vena cava and trachea. | 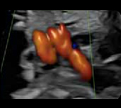 6- Basal view (color Doppler): showing anterograde and symmetrical flows. 6- Basal view (color Doppler): showing anterograde and symmetrical flows. |
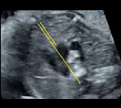 7. Thymus-thoracic ratio(2D): at the 3 vessels and trachea (value) 7. Thymus-thoracic ratio(2D): at the 3 vessels and trachea (value) | 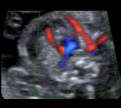 8. Thymus box (color Doppler): showing the inter- nal mammary arteries at the external border of the thymus. 8. Thymus box (color Doppler): showing the inter- nal mammary arteries at the external border of the thymus. |
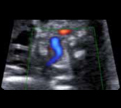 9. Right subclavian artery (color Doopler): showing its normal course in front of the trachea. 9. Right subclavian artery (color Doopler): showing its normal course in front of the trachea. | 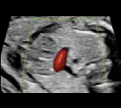 10- Innominate vein (color Doppler): showing its normal drainage into the superior vena cava. 10- Innominate vein (color Doppler): showing its normal drainage into the superior vena cava. |
MODULE 4
Total 11 images x 3 patients = 33 imagesSAGITAL
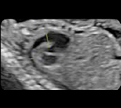 1- Ductal arch (2D): Value and z-scoreof the pulmonary valve and ductus arteriosus 1- Ductal arch (2D): Value and z-scoreof the pulmonary valve and ductus arteriosus | 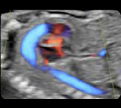 2. Ductal arch (color Doppler): Normal flow (“hockey stick” shape) 2. Ductal arch (color Doppler): Normal flow (“hockey stick” shape) |
 3. Aortic arch (2D): Value and z-score of the ascending aorta, transverse arch and aortic isthmus. 3. Aortic arch (2D): Value and z-score of the ascending aorta, transverse arch and aortic isthmus. | 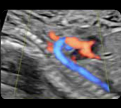 4. Aortic arch (color Doppler): Normal flow (“candy cane” shape) 4. Aortic arch (color Doppler): Normal flow (“candy cane” shape) |
 5. Supra-aortic trunks (2D) (Left carotid-to-sub- clavian distance:value): Common trunk, left carotid artery and left subclavian artery 5. Supra-aortic trunks (2D) (Left carotid-to-sub- clavian distance:value): Common trunk, left carotid artery and left subclavian artery | 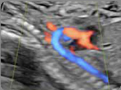 6. Supra-aortic trunks (color Doppler): Normal flow. 6. Supra-aortic trunks (color Doppler): Normal flow. |
 7. Systemic venous return (2D): Superior and inferior vena cava showing their entry into the right atrium. Diameter of inferior vena cava (value and z-score) 7. Systemic venous return (2D): Superior and inferior vena cava showing their entry into the right atrium. Diameter of inferior vena cava (value and z-score) | 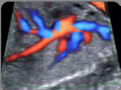 8. Systemic venous return (color Doppler): Normal direction of flow. 8. Systemic venous return (color Doppler): Normal direction of flow. |
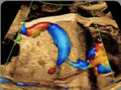 9. Ductus venosus (color Doppler): Confirmation of its drainage at the level of inferior vena cava. 9. Ductus venosus (color Doppler): Confirmation of its drainage at the level of inferior vena cava. | 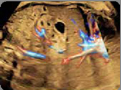 10. Suprahepatic veins (color Doppler): Their confluence at the level of the inferior vena cava (at least two veins). 10. Suprahepatic veins (color Doppler): Their confluence at the level of the inferior vena cava (at least two veins). |
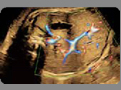 11. Portal system (color Doppler): The normal course of the portal sinus to the right. 11. Portal system (color Doppler): The normal course of the portal sinus to the right. |
MODULE 5
Total 6 images x 3 patients = 18 images
M-MODE
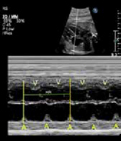 1. Transverse 4-chamber view: Atrial-Ventricular contraction (Heart rate). 1. Transverse 4-chamber view: Atrial-Ventricular contraction (Heart rate). | 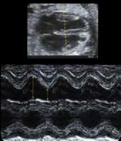 2. Transverse 4-chamber view: Transverse ventricular dimensions (value and z-score) 2. Transverse 4-chamber view: Transverse ventricular dimensions (value and z-score) |
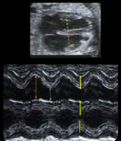 3. Transverse 4-chamber view: Free lateral walls tickness (value and z-score). 3. Transverse 4-chamber view: Free lateral walls tickness (value and z-score). |
PULSED-DOPPLER
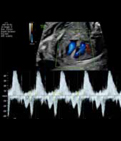 4. Atrioventricular interval: Inflow and outflow of the left ventricle (value) from the onset of the “A” mitral wave to the onset of the aortic wave. 4. Atrioventricular interval: Inflow and outflow of the left ventricle (value) from the onset of the “A” mitral wave to the onset of the aortic wave. | 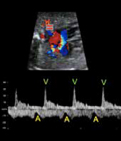 5. Atrioventricular interval: Pulmonary artery-vein from the onset of the “A” wave on the pulmonary vein to the onset of the pulmonary artery wave. 5. Atrioventricular interval: Pulmonary artery-vein from the onset of the “A” wave on the pulmonary vein to the onset of the pulmonary artery wave. |
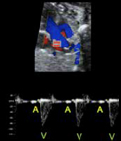 6. Atrioventricular Interval (Aorta-cava): From the onset of the “A” wave on the superior vena cava to the onset of the aortic wave. 6. Atrioventricular Interval (Aorta-cava): From the onset of the “A” wave on the superior vena cava to the onset of the aortic wave. |
MODULE 6
Total 9 images x 3 patients = 27 images
RIGHT CARDIAC FUNCTION
2D-ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
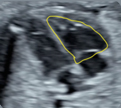 1. Right ventricle fractional area Change (FAC): End-di- astolic área (value and z-score) FAC = (end-diastolic area – end-systolic area)/end-diastolic area *100. 1. Right ventricle fractional area Change (FAC): End-di- astolic área (value and z-score) FAC = (end-diastolic area – end-systolic area)/end-diastolic area *100. | 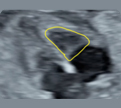 2. Right ventricle fractional Area Change (FAC): end-systolic area (value and z-score). FAC = (end-dias- tolic area – end-systolic area)/end-diastolic area *100. 2. Right ventricle fractional Area Change (FAC): end-systolic area (value and z-score). FAC = (end-dias- tolic area – end-systolic area)/end-diastolic area *100. |
PULSED-DOPPLER
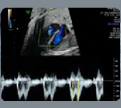 3. Tricuspidflow: E/A velocities (value). 3. Tricuspidflow: E/A velocities (value). | 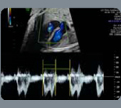 4. Tricuspid flow: filling time fraction (FTF) (value and z-score). FTF = filling time/cycle time)*100 4. Tricuspid flow: filling time fraction (FTF) (value and z-score). FTF = filling time/cycle time)*100 |
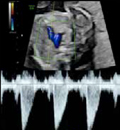 5. Pulmonary flow: Systolic peak velocity (Value). 5. Pulmonary flow: Systolic peak velocity (Value). | 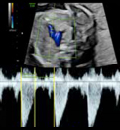 6. Pulmonary flow: ejection time Value and z-score. ETF = ejecting time/cycle time)*100 6. Pulmonary flow: ejection time Value and z-score. ETF = ejecting time/cycle time)*100 |
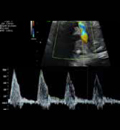 7. Ductus arteriosus pulsatility index: Value and z-score. 7. Ductus arteriosus pulsatility index: Value and z-score. | 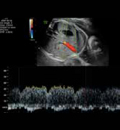 8. Ductus venosus pulsatility index: systolic, early diastolic and atrial contraction Values. 8. Ductus venosus pulsatility index: systolic, early diastolic and atrial contraction Values. |
M-MODE
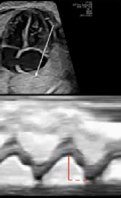 9. TASPE:Tricuspid annular plane systolic (value and z-score) 9. TASPE:Tricuspid annular plane systolic (value and z-score) |
MODULE 7
Total 10 images x 3 patients = 30 images
RIGHT CARDIAC FUNCTION PULSED-DOPPLER:
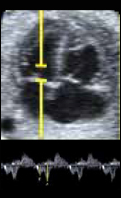 1. Mitral flow: E/A Value. 1. Mitral flow: E/A Value. | 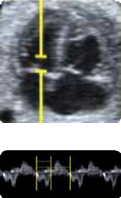 2. Mitral flow: Filling time fraction (value and z-score).FTF = filling time/cycle time)*100 2. Mitral flow: Filling time fraction (value and z-score).FTF = filling time/cycle time)*100 |
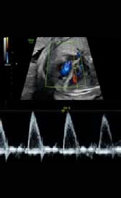 3. Aortic flow: Systolic peak velocity (value). 3. Aortic flow: Systolic peak velocity (value). |  4. Aortic flow: Ejjection time fraction (value and z-score). ETF = ejection time/cycle time)*100 4. Aortic flow: Ejjection time fraction (value and z-score). ETF = ejection time/cycle time)*100 |
 5. Myocardialperformanceindex: Isovolumic contrac- tion, ejection and isovolumic relaxation times (value and z-score).MPI = isovolumetric contraction time + isovolumetric relaxation time)/ejection time. 5. Myocardialperformanceindex: Isovolumic contrac- tion, ejection and isovolumic relaxation times (value and z-score).MPI = isovolumetric contraction time + isovolumetric relaxation time)/ejection time. |  6. Aortic isthmus pulsatility index: (value and z-score). 6. Aortic isthmus pulsatility index: (value and z-score). |
 7. Pulmonary veins flow: Systolic, early diastolic and atrial contraction velocities. (values). 7. Pulmonary veins flow: Systolic, early diastolic and atrial contraction velocities. (values). |
M-MODE
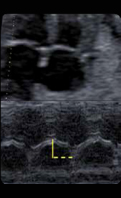 8. MASPE: Mitral annular plane systolic (value and z-score). 8. MASPE: Mitral annular plane systolic (value and z-score). | 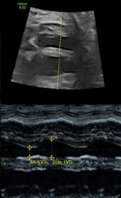 9. Left ventricle ejection fraction (EDV = (7/(2.4/EDD)) xEDD3) y systole (ESV = ((7/(2.4/ESD))xESD3): Ejection fraction = (EDV – ESV)/EDV. (EDV: end-diastolic vo- lume, ESV: end-systolic volume, EDD: end-diastolic dimension, EDS: end-systolic dimension. 9. Left ventricle ejection fraction (EDV = (7/(2.4/EDD)) xEDD3) y systole (ESV = ((7/(2.4/ESD))xESD3): Ejection fraction = (EDV – ESV)/EDV. (EDV: end-diastolic vo- lume, ESV: end-systolic volume, EDD: end-diastolic dimension, EDS: end-systolic dimension. |
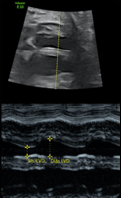 10. Left ventricle shortening fraction: Shortening fraction = (End-diastolic dimension – End-systolic di- mension)/End-diastolic dimension * 100. 10. Left ventricle shortening fraction: Shortening fraction = (End-diastolic dimension – End-systolic di- mension)/End-diastolic dimension * 100. |
MODULE 8
Two cases of CHD which must be well documented. The diagnosis must be justified by showing the specific features of the cardiac defect. In addition, the counselling to the pregnant woman must be also explained.
MODULE 9
One case of CHD which must be well documented. The diagnosis must be justified by showing the specific fetaures of the cardiac defect. In addition, the counselling to the pregnant woman must be also explained.
5-FACE TO FACE IN CLINIC
The face-to-face period consists of two weeks (two periods of one week each) in the the department of perinatal medicine will be included. The first week will take place halfway through the course in order to expand knowledge, improve skills on echocardiography and facilitate interaction with mentors, faculty members and colleagues. The second week is scheduled at the end of the postgraduate to consolidate knowledge and improve understanding on more advanced techniques.First week calendar: ???????? and second weeks: ????????????????. During these two periods the participants will have the opportunity to meet the faculty and their mentors. The stays will include the following activities:
- “Meet the professor” sessions that enable personal discussion on the most relevant aspects of each module, based on clinical cases, with the faculty members.
- Invited lectures from international experts on a specific topic of interest including basis of fetal cardiac magnetic resonance, core aspects on the assessment of the right ventricle, electrocardiogram, genetics in CHD, impact of CHD on neurodevelopment, fetal-neonatal transition and fetal cardiac programming. This will enable interaction with the postgra duate faculty members and also with invited professors from other universities experts in a specific topic of interest.
- Practical training. Dedicated sessions with volunteer patients, with hands-on fetal ec- hocardiography with reduced number of attendees, enabling to teach tips and tricks for both structural and functional
- Specific meet with the mentor sessions in order to discuss any doubt on specific topics and to define and plan the research work (fist onsite week at mid-course).
- Defense of the research work, enabling the discussion with colleagues and the faculty members (second onsite week at the end of the postgraduate training).
6-RESEARCH PROJECT (MODULE 10)
The postgraduate training includes the completion of a research work that will be evalu- ated by the committee. The research work usually includes a critical literature review of a specific topic that can be complemented by original data from the student’s institution. The research work is conducted personally by the student, under the guidance and supervision of a mentor. The topic is chosen and planned during the first onsite week and defended at the second onsite week.
PRESENTATION & FORMAT
Deadline and submission method: The deadline for the research project’s submission will be during the last on-site week (??????). The project must be submitted in a PDF format. Failure to submit it within the defined period of time limit means suspending the task
FORMAT: The text must be formatted with 1.5 line spacing, Arial font, and size 12.
a) Margins: The margins must be set to: Upper: 2 Lower: 2 cm. Left: 4 cm. Right: 2 cm.
b) Page numbering: Starting with the introduction, all pages must be numbered on the top-right side.
c) Tables: They must be clear, numbered with Arabic numerals in relative order, titled cle- arly stating their content, be self-explanatory and avoid duplicating content in the text.
d) Graphs: They must be clear, numbered with Arabic numerals in relative order, titled clearly stating their content, be self-explanatory and avoid duplicating content in the text or tables.
e) Figures: They must be numbered with Arabic numerals in a relative order and have a short If the image or the photo has been published previously, the origin must be mentioned in the title with appropriate citation of the reference.
CONTENTS OF THE RESEARCH PROJECT
1. COVER
2. INDEX
3. ABSTRACT
4. STATE OF THE ART – INTRODUCTION
5. HYPOTHESIS AND OBJECTIVES
6. MATERIALS AND METHODS
7. RESULTS
8. DISCUSSION
9. CONCLUSIONS
10. REFERENCES
11. ANNEXES AND APPENDICES
GUIDELINES FOR DEVELOPMENT OF THE RESEARCH PROJECT
1. SUMMARY
It must be written in English. It must demonstrate in a concise way the hypothesis and the obtained results. The abstract must have a maximum of 350 words and be written in a structured format including the following parts:
- Introduction: Define the problem and the aim of the project.
- Materials and methods: Describe how the project was done.
- Results: Describe briefly the main results of the project.
- Conclusions: Report the main findings of the results and the clinical implications, if relevant.
2. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This section contextualizes the project developed within the current framework of knowledge. It must be less than 10 pages long. It must clearly establish the problem being investigated, the current knowledge about it and the motivation for further research. It must summarize the relevant previous studies carried out on the subject and explain how this project is different from the prior. The theoretical framework must be strongly supported by recent scientific literature (preferably no older than 10 years).
3. HYPOTHESIS AND OBJECTIVESA
Short affirmative sentence that could be accepted or rejected in an experimental or a clinical research.
- General objective: It must start with an infinite verb (To .., To analyze…, To know…) and it must be written in a way that implies the steps needed to prove the proposed hypothesis.
- Specific objectives: They must be numbered according to the stages of the project. They must be written as actions that, when executed consecutively, will allow the different stages of the project to be carried out, with the aim of accepting or rejec- ting the hypothesis of the project.
4. MATERIALS AND METHODS
This section must be written in the past tense, indicating:
- Type of study: experimental, descriptive, prospective,
- Sample: Detailed description of the study sample, how it was obtained, source, characteristics, size, etc.
- Procedures: The methods and procedures must be clearly described. The measure- ment instruments (if any) must be included as annexes at the end of the project. If methods or techniques from other authors have been used, they must be described briefly with the citation of the corresponding reference. It must be clearly stated how each of the specific objectives will be carried out.
If applicable, this section of the project must also include an explanation of the statistical approach used to analyze the data, as well as the software used for such purpose.
5. RESULTS
The research findings must be written in an objective and clear way, ideally following the order of the specific objectives and methodology. The data must be analyzed in tables, graphs, figures or images. Each of them must include an explanatory text. This section must not include the interpretation of the results, this will appear in the discussion section.When the research project compares original results with the results of other authors, the source of the compared data must be clearly explained. When a statistical analysis is included, the results must clearly state which variables are statistically different.
6. DISCUSSION
This section describes the meaning of the obtained results, in the context of what is known about the studied topic. The proposed hypothesis must be discussed and accepted or rejected. Emphasis should be given to the new and important findings of the study. The research findings must be compared with previously published studies.The limitations of the experimental methods must be discussed, as well as the possible implications for future studies. When appropriate, the clinical relevance of the results must be included.
7. CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions must be written as a series of short sentences, based directly on the obtained results and the experimental or clinical evidence of the project. Speculation from other projects must be avoided.
8. REFERENCES
Citations and references must follow Vancouver style.
9. ANNEXES AND APPENDICES
All the documents that are considered relevant for the research project must be included in this part. They should be cited in the text in the corresponding section and proper- ly numbered.
7-EVALUATION CRITERIA
The evaluation of the postgraduate degree in Fetal Cardiology is based on a continuous evaluation. In order to obtain the final degree, all the parts must have been passed separa- tely (theoretical exams, practice at home, clinical cases, research project, participate in the forum and final exam) within the agreed dates. Failure to comply with this rule for whatever reason involves suspending the degree.
Resits: There will be only one opportunity to resit failed modules or tasks. The maximum grade that can be obtained in resits will be the minimum grade set as required to approve. This regulation does not allow exceptions of any kind.The non-approval of a module means the failure to obtain the course degree. The pos- sibility of enrolling in the next year of the pending module(s) is offered, provided that the number of modules suspended is not greater than two but requires payment of the module and all corresponding university fees. In the event of suspending more than two modules there will be no option to recovery, and you would have to enroll in the training again and complete it in full.The different evaluable points of the course are described below:
ONLINE EXAMS OF THE THEORETICAL MODULES
The aim of these exams is to explore the level of knowledge acquired in relation to the con- tent explained in the theoretical classes. They consist of multiple-choice questions test with only one valid answer per question. The different exams are composed of 15 questions.
Minimum Score: The minimum score to pass the self-assessment exams is 70%.
Duration: There is a time limit of 5 hours per exam. Time starts counting at the moment of accessing the test and continues to progress despite disconnecting from the application.The test can be repeated 5 times with a time interval between attempts of 4 hours. Despi- te having passed the exam, it can be repeated in order to continue learning and improving the obtained score. The system will consider the best score among the attempts.The average score of all the self-assessment exams of the different modules will have an impact on the overall score of the course contributing by 25%. It is necessary to pass each module to be able to calculate the average. The exam must be carried out during the time period defined in the WEB.
PRACTICE at Home
The images of the practice must be submitted within the requested deadlines in order to be evaluated. To obtain the final postgraduate degree this part must be passed.Any submission after the deadline will entail the non-evaluation of the practice and will be considered as failed. There will be a recovery period at the end of the postgradu ate degree.The students will have a calendar with the practice at home’s submission deadlines and the expected dates to receive the practice at home scores from the teaching staff.The final score of the practice at home will be obtained by calculating the average of the 9 sub missions and will correspond to 25% of the overall score.
Resits: There will be a second opportunity to resubmit any failed practice at home, either for not having submitted it prior to the deadline or for not having reached the necessary score to pass. The maximum score that can be obtained in the recovery will be 70%. If the student fails the resit, there will be no more chance of resubmission, and therefore, it will not be possible to obtain the final certificate of the ‘postgraduate degree in Fetal Cardiology.
Deferrals: If the student is unable to submit a task of a module, always before the stated date, an extension can be requested by filling out a form available on the WEB for consideration by the teaching coordinator. Extensions of deadlines will only be accepted for larger and justifiable reasons.
RESOLUTION OF CLINICAL CASES, FORUM CONTRIBUTION AND MASTERCLASSES
The participation in the forum will be evaluated continuously throughout the course. Those contributions that provide answers to the questions raised in the clinical cases and the doubts generated by the rest of the participants will be positively valued. This part represents 10% of the final score.
RESEARCH PROJECT
To obtain the final postgraduate degree this part must be passed and it will correspond to 20% of the overall score.To set the final project score, the evaluation criteria described above will be followed. To approve the final project, a minimum grade of 7 will be required.
- Evaluation criteria (Maximum score):
- RELEVANCE OF THE PROPOSAL: Is the developed project relevant? 0,5
- ORIGINALITY OF THE PROPOSAL: Is the developed research project original? 0,5
- DRAFTING OF THE PROJECT: Is the project WELL written and follows the scien- tific standards? 1
- OBJECTIVES: Are the objectives clearly defined and stated? 0,5
- HYPOTHESIS: Is the hypothesis clearly established? 1
- MATERIALS AND METHODS: Are the methods used in the development of the project appropriate? 1
- RESULTS: Are the data properly and clearly presented?
- DISCUSSION: Are the obtained results critically analyzed? Are they properly com- pared to the existing literature on the topic? 0,75
- CONCLUSIONS: Are the conclusions based on scientific evidence? 0,5
- REFERENCES: Are the project references written correctly? Are the references updated and relevant to the subject? 0,25
- TOTAL SCORE: 10
FINAL EXAM The aim of the final exam is to explore the level of knowledge acquired in the postgraduate degree. It will correspond to 20% of the overall score. It consists of 50 multiple-choice questions test with only one valid answer per question.
Minimum Score: The minimum score to pass the self-assessment exams is 70%.
Duration: There is a time limit of 2 hours. Time starts counting at the moment of acces- sing the test and continues to progress despite disconnecting from the application. The test can be repeated 5 times with a time interval between attempts of 3 hours. Despite having passed the exam, it can be repeated in order to continue learning and improving the obtained score. The system will consider the best score among the attempts.The exam must be carried out during the time period defined on the WEB.
FINAL EVALUATION
| Average of the module’s exams | 25% |
| Average of the practice at home | 25% |
| Clinical cases and Forum contribution | 10% |
| Research project | 20% |
| Final exam | 20% |
| TOTAL | 100% |
GRADING DEGREE
| Score | Grade | Comment |
| 0 – 6.9 | Fail | |
| 7 – 7.9 | Approved | |
| 8 – 8.9 | Very good | |
| 9 – 10 | Excellent | The top two overall scores (as long as they are above 9) will be graded with an honor mention. |
aaaaa
The students will be awarded two certificates:
- A university “Postgraduate Degree in Fetal Cardiology”. The title will be issued by the Institute of Continuing Education of the University.
- Certificate in Fetal Cardiology from the University

Table of Contents